Leaving Community
Are you sure you want to leave this community? Leaving the community will revoke any permissions you have been granted in this community.
Creating a dkNET Authentication Report
For NIH grant applications, dkNET can assist you in preparing authentication plans for cell lines or antibodies to comply with the NIH Submission Policy. View an example of authentication plan here, prepared by Dr. Anita Bandrowski, University of California San Diego.
Below is general information on best practices for authenticating cell lines and antibodies. dkNET has also created an automated tool to enable researchers to create a customized report based on the cell lines and antibodies they plan to use. These customized reports provide additional information such as known problems with a particular cell line or antibody. If you wish to use dkNET tools to create a dkNET Authentication Report, click Start here
Basic Authentication Information Without Creating an Authentication Report
Cell Line Authentication Plan Information
The authentication plan for the cell lines is based on the International Cell Line Authentication Committee (ICLAC)'s "Cell Line Checklist for Manuscripts and Grant Applications"(1).
-
Check dkNET for Misidentified Cell Lines
If you have not created a dkNET Authentication Report, you can check for this information via dkNET Resource Reports.
Check Resource InformationTo verify that this is not a false cell line, misidentified, or to check this is known to be an authentic stock, please check via dkNET. dkNET obtains this information from Cellosaurus (2).
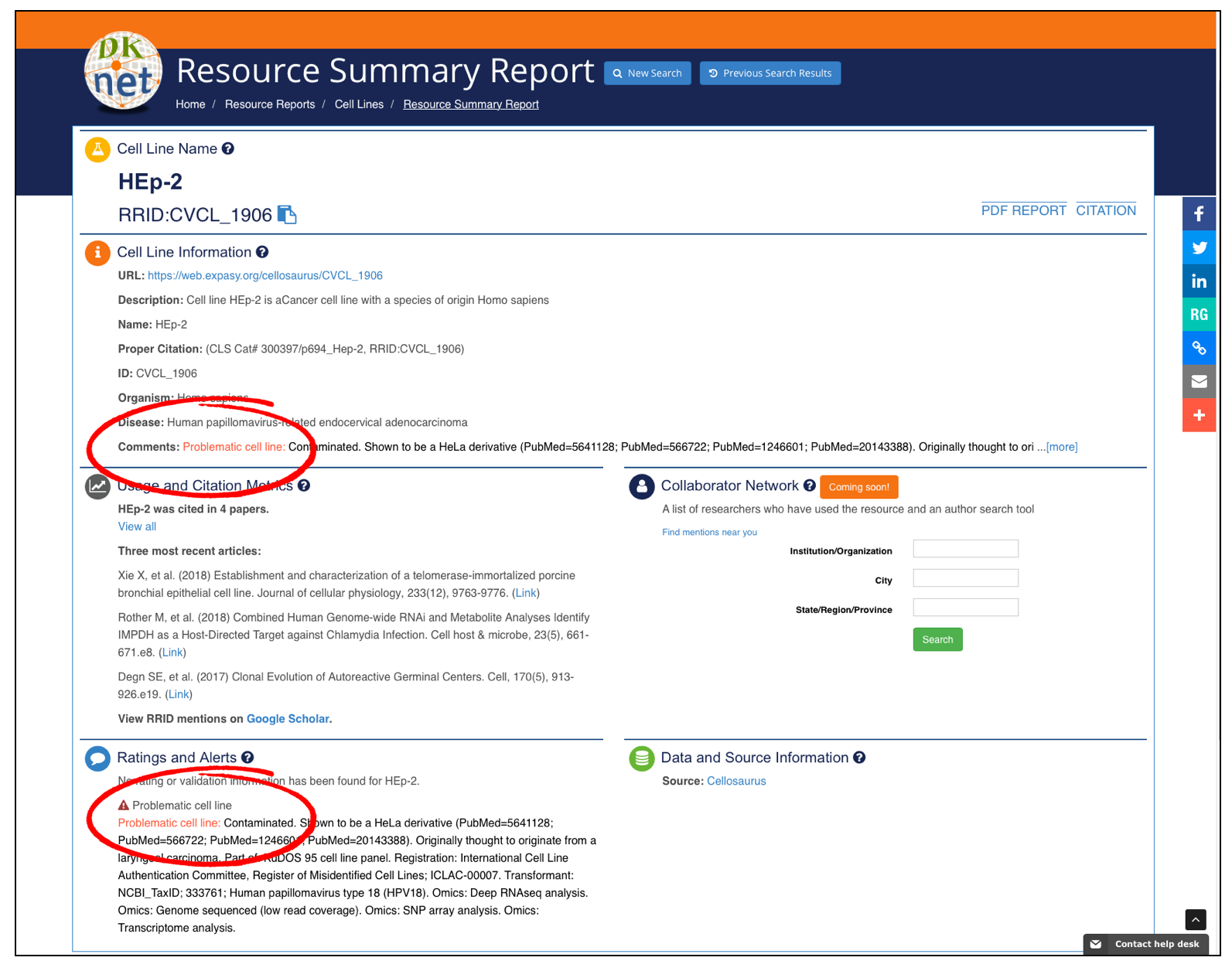
Click to enlarge -
Provide the following information in the Authentication of key biological and/or chemical resources attachment(3) in the grant application:
-
Identification of cell lines
-
Provide Name, Vendor, Catalog#, RRID (Find RRID via dkNET Resource Report)
-
If you can't find your cell lines in the system, please register it at Cellosaurus(2). An RRID will be generated in 1-2 business day.
-
-
Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Profiling
The gold standard for authentication testing of cell lines is STR profiling. STR profiling should be performed and compared to results from donor tissue, or to online databases of cell line STR profiles. Authentication testing should be performed on established cell lines regardless of the application, and the test method and results included in the Materials and Methods section of any research publication. Testing should be done, at minimum, at the beginning and end of experimental work(4, 5).
-
Sources:
- Cell Line Checklist for Manuscripts and Grant Applications, International Cell Line Authentication Committee (ICLAC), version 1.2, updated on May 9, 2014.
- Cellosaurus (https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/) is a cell line knowledge resource and nomenclature authority. Cellosaurus covers the information of "ICLAC register of misidentified cell lines" (latest version 8.0, released Dec. 1, 2016,) and provides more updated information.
- Guidance: Rigor and Reproducibility in Grant Applications
- Standards for Cell Line Authentication and Beyond, The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
- Published standard: ANSI/ATCC ASN-0002-2011, Authentication of Human Cell Lines: Standardization of STR Profiling, American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
Antibody Authentication Plan Information
This authentication plan for antibodies is based on the methods suggested in "A proposal for validation of antibodies" (Uhlen M et. al., 2016)(1), the guideline published in the Journal of Comparative Neurology (Saper C, 2005)(2), and the Example Authentication of of Key Biological and/or Chemical Resources (Bandrowski A)(3).
-
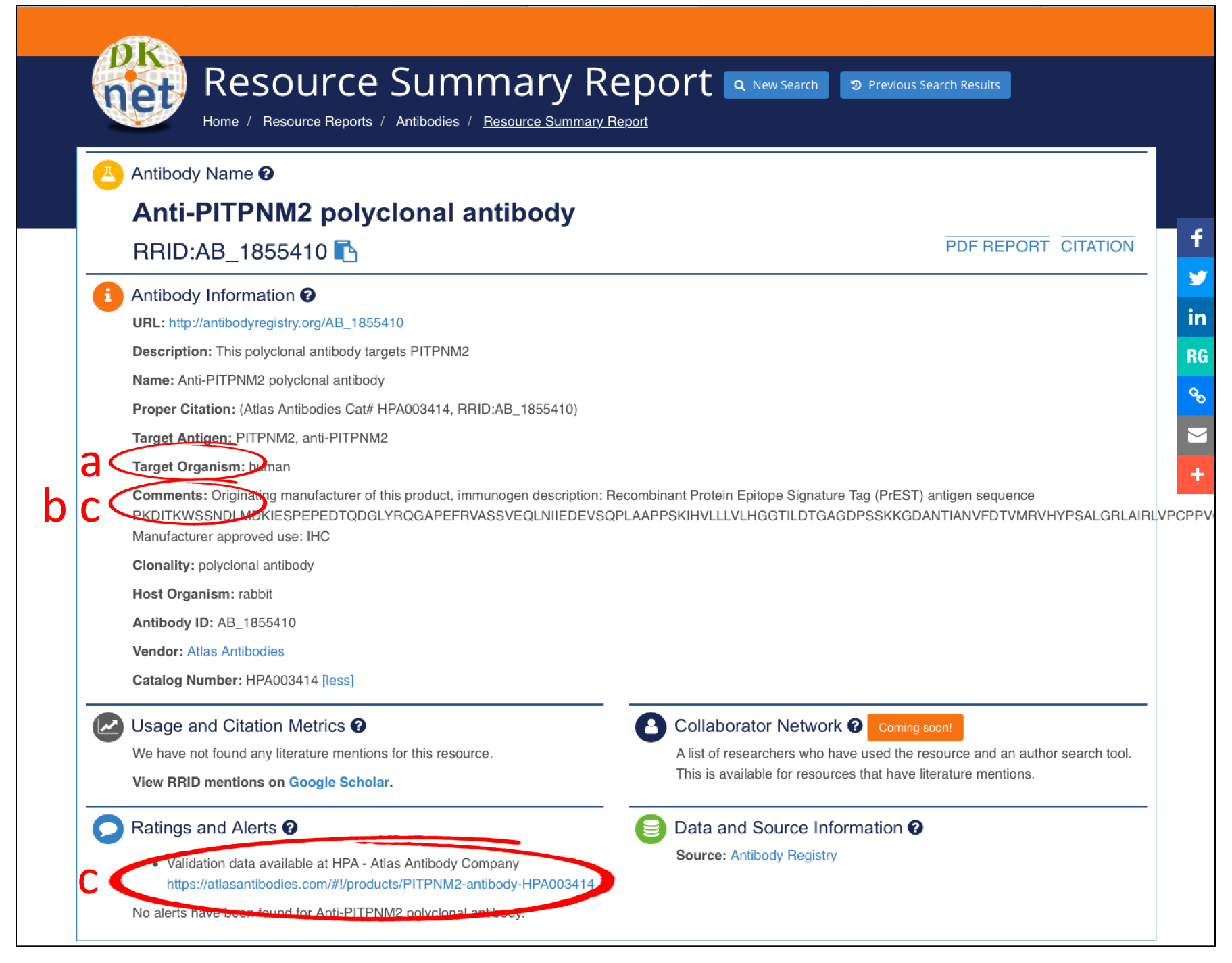
Check dkNET for Known Issues in Antibodies
If you have not created dkNET Authentication Reports, you can check the following information at dkNET Resource Reports.
Check Resource InformationPlease check your antibody information at dkNET to determine whether there are any known issue. dkNET obtains this information from the Antibody Registry(4).
-
Provide the following information in the Authentication of key biological and/or chemical resources attachment(5) in the grant application:
-
Identification of antibodies
-
Provide Name, Vendor, Catalog#, RRID (Find RRID via dkNET Resource Report)
-
If you can't find your antibody in the system, please register it at Antibody Registry(4). An RRID will be generated in 1-2 business day.
-
-
Validation
-
Antibody validation must be carried out in an application- and context-specific manner (Uhlen et al., 2016), i.e., just because you used an antibody successfully in one application, doesn’t mean it will translate. To validate an antibody, it must be shown to be specific, selective, and reproducible in the context for which it is to be used (Bordeaux et al., 2014). See ii. Suggested validation methods. When selecting an antibody to use, pay special attention to the following:
Check Resource Information-
Check Target Organism - Check to see if the antibody has been developed for and tested in the target species for your experiment in the Target Organism field.
-
Check Application - Check if your planned applications included in the recommended applications provided by the vendor listed in the Comments field. We do not recommend using an antibody that has not been tested for a specific application.
-
Check Validation Information - Check validation information to see if it is a widely used reagent or if any concerns have been raised.
-
- Suggested validation methods based on applications(1)
Click to enlarge
-
-
Sources:
- Uhlen M et. al. A proposal for validation of antibodies. Nature Methods, Oct;13(10):823-7. 2016.
- Saper C. An open letter to our readers on the use of antibodies. Journal of comparative neurology, 493(4):477-8, 2005.
- Bandrowski A. Example Authentication of of Key Biological and/or Chemical Resources, NIH Policy on Rigor and Reproducibility Section, UC San Diego Library website.
- AntibodyRegistry (https://antibodyregistry.org)
- Guidance: Rigor and Reproducibility in Grant Applications, National Institute of Health Office of Extramural Research Website.
Please note that for NIH grant applications, the plan should be no more than one page. You can copy and paste the information and edit the information in a word file.
Create Authentication Reports
The following information is included in the report:
- Resource information (the current system is limited to antibodies and cell lines. Additional resources will be added in the future)
- RRIDs, which are used as unambiguous identifiers of the resources
- Any noted issues or problems with the resources
- An authentication plan based on submitted information
Go to Authentication Reports Dashboard to begin the process or view my Authentication Reports
An example of Authentication Report

Click to enlarge
*Disclaimer: Researchers should verify the authenticity of their research resources before grant submission or publication. Current NIH guidelines do not include clear instructions for the authentication process. Our recommendations for authenticating the resources on dknet.org are based on experts’ opinions and suggestions from volunteer working groups. Information provided on dknet.org does not represent NIH policy. dkNET ingests resource identification information from relevant databases in a timely manner, but timeliness may vary by resource center. For the most current information, please check individual resource centers directly. dkNET bears no responsibility for the accuracy and reliability of ingested content.